Urine Test: What Can It Detect?
A urine test can look at various variables. Its main purpose is to determine the presence or absence of certain components of urine. This information is essential for a correct diagnosis.
A urine test is a test performed in the laboratory to look for different types of health disorders. During this test, a professional checks the appearance, concentration, and content of urine. The results may suggest a medical condition. The doctor will then confirm the diagnosis using other methods.
It should also be mentioned that the urinalysis by itself does not make a clear diagnosis. The physician must interpret the implications of the analysis of the results. These types of tests are carried out because of the disorders that you have, as well as to prevent or control them.
Testing your urine can detect substances that your body is unable to retain or needs to remove. As little as 10 milliliters of urine is needed for a doctor to be able to obtain evidence of many diseases. These include, for example, diabetes, multiple myeloma and kidney failure.
When do doctors ask for a urine test?
Typically, doctors require a urine test to:
- Assess the function of the kidneys. Urine specific gravity can help determine whether the kidneys are functioning properly or not.
- Detection of the presence of bacteria. If a urinary tract infection is suspected, your doctor will perform a urine test to look for the presence of bacteria and / or certain types of bacteria in your urine sample.
- Detection of the presence of certain substances. Healthy people should not contain certain components in the urine. However, if they are present in it, they may indicate the existence of a health disorder.
- Assess the impact of specific diseases or medications. The presence or level of certain components of urine can help determine whether the patient’s condition has worsened or improved. It also indicates whether the medications you are taking have side effects.
Urine test and its types
There are different types of urine test. We distinguish them depending on the way they are performed and their purpose. Typically, the doctor recommends performing:
- Uroscopy. It consists in visually assessing the appearance of urine. Color, turbidity, and odor are important, but ambiguous, data.
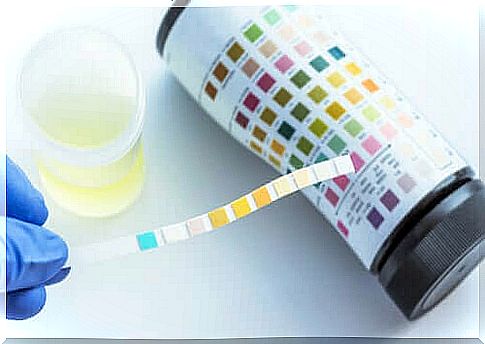
- Strip test. This test is carried out by pouring a small amount of urine onto a special strip on which the appropriate chemical components are placed. These stripes react to the presence of certain substances in the urine and change color.
- Urine sediment tests. It is carried out in a laboratory by separating the liquid components from the solids in the urine. The solid substances are then examined under a microscope to see if they contain specific particles or cell fragments.
- Biochemical research. Such tests are also carried out in the laboratory. They make it possible to check whether there are certain substances or particles in the urine that indicate the presence of certain diseases. They provide a more in-depth analysis where lab technicians use different biochemical techniques.
- Microbilogical research. With these tests, you can determine if an infection has developed and find out what bacteria are carrying it.
What can be detected by a urine test?
Typically, your doctor will recommend a general urine test to check for any unusual features. Healthy urine is clear and does not smell too strongly. If it is cloudy or has a very pungent odor, something may be wrong.
Then a strip test is performed. If you put a small amount of urine on the strip, it will not change color if the urine is healthy. If, in turn, there are substances in it that should not be there, the bar will change color.
This tool detects:
- Acidity or pH. If it is not normal, it may indicate problems with the functioning of the urinary tract or kidneys.
- Density. High density is one of the symptoms of dehydration.
- The presence of protein. Elevated protein levels indicate kidney problems.
- Glucose level. If there is glucose in your urine, it may indicate the development of diabetes.
- Ketone bodies. They also suggest the development of diabetes, especially decompensation, which can be very serious.
- Bilirubin. Its presence suggests the possibility of liver damage or liver disease.
- The presence of blood. It may indicate the development of an infection, kidney damage, kidney stones, or cancer of the kidney or bladder. This is a symptom that requires additional tests to help make a correct diagnosis.
- Nitrite or leukocyte esterase. They suggest the development of an infection.
The presence of certain components in the urine requires further laboratory testing, such as urine sediment testing, biochemical testing, and microbiological testing. Your doctor will decide what steps to take.
Adherence to medical recommendations and not skipping any steps is crucial. Remember that you must seek medical advice if you have any disturbing urinary symptoms.