The Effect Of Depression On The Brain – 4 Symptoms

What is the effect of depression on the brain ? Well, huge! While it is widely believed that the disease has a negative effect on our emotional state and well-being, sufferers can also suffer from a variety of physical ailments and significant changes in the brain.
These, in turn, affect the work of the entire organism. Importantly, depression has now reached the dimensions of a global phenomenon – more and more people around the world are struggling with its symptoms every day. According to the estimates of the International Health Organization (WHO), more than 300 million people worldwide suffer from depression.
The next data are even more alarming. About 800,000 patients, unable to cope with their own emotions, commit suicide. The disease is also the most common cause of death among young people between 15 and 29 years of age.
The impact of depression on the brain is therefore enormous and this disease should not be underestimated in any case. It is imperative to realize that it is not just a fleeting ailment, a bad day or a decline in form.
The Effects of Depression on the Brain – Basic Information
We can all have a bad day from time to time. However, when it goes on for weeks or even months, it’s time to take action.
In most cases, depression does not go away on its own and you need to see a specialist. Let us not be ashamed of what is happening to us, and try to overcome the depression that has overwhelmed our entire body as soon as possible.
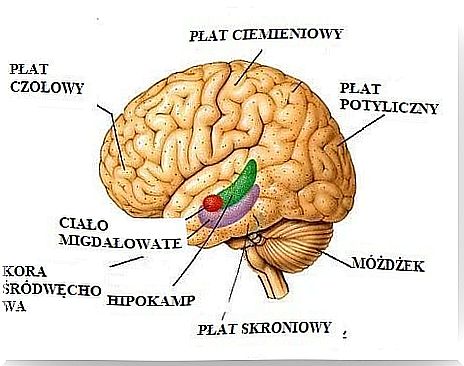
Moving on specifically to the brain and how it works in someone with depression, let’s start with some basics. Well, the disease directly affects three areas of the brain: the hippocampus, the amygdala, and the prefrontal cortex. In addition, the body is less oxygenated during this disease.
You will find more detailed information on this below.
1. Shrinkage of the hippocampus
The hippocampus is located in the central part of the brain. It is responsible for memory, information storage, and regulating the production of cortisol, commonly known as the stress and happiness hormone.
When we are under physical or mental stress, including depression, the body begins to produce increased amounts of cortisol to combat the effects of stress. However, when levels of this hormone reach really high levels, a chemical imbalance occurs in the brain.
As a consequence, the production of neurons decreases and the hippocampus begins to contract.
2. The effect of depression on the brain: Shrinkage of the prefrontal cortex
The prefrontal cortex is located at the front of the brain and is responsible, among other things, for regulating our emotions and creating memories.
As a result of severe stress, like the hippocampus, it also begins to shrink and shrink in volume. According to the researchers, a lack of empathy and postnatal depression stem from this part of the brain.
3. Inflammation of the amygdala
The amygdala is located in the temporal lobe, in the lower central part of the brain. Its primary function is to regulate emotions such as pleasure, happiness as well as fear.
Excess cortisol also negatively affects this part of the brain. It leads to the development of inflammation of the amygdala and increases its activity, which in turn causes problems with falling asleep and activates abnormal patterns of behavior.
Moreover, the hyperactivity of the brain’s amygdala is linked to various glands in the body, which also release more hormones than normal due to excess stress and lead to a variety of health problems.
4. Inadequate oxygenation – the little-known effect of depression on the brain
In addition to the direct changes that depression causes in the human brain, there are a number of other factors that indirectly affect brain function.
Scientific research proves that the body of a person struggling with depression is much less oxygenated than in healthy people. It is not entirely clear whether this is due to changes in the way we breathe, or whether it is caused by something else.
How does depression affect the brain with the rest of the body?
The brain changes described above don’t happen suddenly overnight. They are the result of long-term depression. Research shows that modifications in the chemical composition of the hypothalamus and prefrontal cortex take 8-10 months to develop.

Dr. Thomas Frodl, a scientist at a hospital in Magdeburg, Germany, followed patients with depression for three years. He wanted to find out how depression affects the brain. One of the conclusions he has come to is that there is no doubt that the degeneration of a patient’s brain worsens with time as depression progresses.
The physical and chemical changes induced in the brain by developing depression can lead to problems with concentration, sleep disturbances, cognitive decline, fatigue, and other conditions that reduce the quality of everyday life.
Here are some of the consequences depression can have on the human brain:
- Memory impairment
- Lowering the efficiency of neurotransmitters
- Stagnation of brain development
- Decreased learning ability
- Cognitive problems
- Mood changes
- Lack of empathy towards others
- Insomnia
- Tiredness
How can depression be reduced to the brain?
Research findings suggest that the main cause of emotional and physical changes in the brain is a chemical imbalance caused by an excess of cortisol and other chemicals in the body.
For this reason, therapeutic treatments are recommended to regulate the production of hormones such as cortisol and serotonin. Medicines or therapeutic therapy can be used for this.

Undoubtedly, one of the best and most effective methods of overcoming depression is psychotherapy. Thanks to it, most patients recover to full emotional and mental health. Hence, it is so important to start treatment after detecting symptoms in yourself or a loved one.
There are also many healthy habits that a person struggling with depression can adopt on their own. Their goal is to deal with this disease faster. In addition, they have a very positive effect on the functioning of our brain. These include, among others:
- Ability to deal with stress, for example by using relaxation techniques
- Regular physical activity
- Good sleep and care for sleep hygiene
- Avoiding alcohol, drugs and other intoxicating substances
In summary, depression is a disease that goes much further than simply changing your mood. While it is not visible at first glance, the brain also acutely experiences changes on the physical and chemical levels. And this, in turn, has a wide impact on the work of the whole organism.