Kidney Acidosis – Find Out What It Is And How It Arises
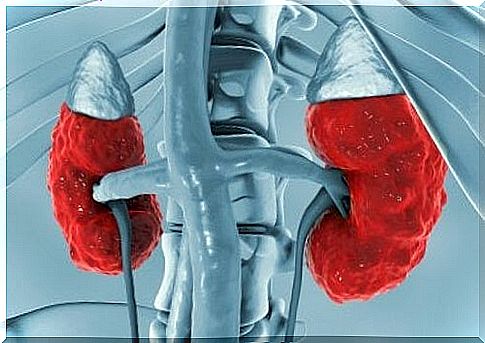
Hyperchloremic kidney acidosis is caused by the body losing too much sodium bicarbonate . In addition, when you are in this condition your kidneys do not remove enough acid from your body.
This disorder is characterized by a reduction in the ability of the proximal tubules to reabsorb bicarbonate from the glomerular filtrate, resulting in hyperchloraemic renal acidosis of a metabolic nature.
The exact extent of this disorder is not known exactly. However, drug-induced proximal renal tubular acidosis (ATRp) is relatively common. On the other hand, isolated hereditary renal hyperchloraemic acidosis is very rare.
What are the symptoms of hyperchloraemic acidosis of the kidneys
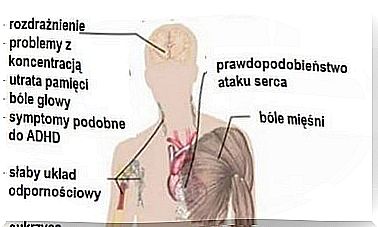
The symptoms of hyperchloraemic renal acidosis depend on the underlying disease or condition. This disorder causes rapid breathing, lethargy, or confusion. In addition, it can lead to shock and even death.
Initially, it appears at a very low urine pH due to unabsorbed bicarbonate ions. There is also growth retardation and decrease in bone mineral density due to hyperchloraemic renal acidosis.
Hypokalaemia may occur in some cases and symptoms of periodic paralysis may occasionally appear. On the other hand, rickets and osteomalacia are rather caused by vitamin D deficiency and lack of phosphate reabsorption.
The causes of the disease
Hyperchloraemic renal acidosis can occur as a result of some kind of kidney disease , such as distal renal acidosis and proximal renal tubular acidosis.
Hyperchloraemic renal acidosis can be acquired or inherited recessively in most cases, but it can also be the result of dominant inheritance. Acquired renal acidosis is caused by a mutation in the SLC4A4 gene (4q13.3).
However, acidosis acquired in dominant heredity is caused by mutations in an unidentified gene. The tubule closer to the urinary tract absorbs about 80% of the filtered bicarbonate load, but its defect causes a loss of bicarbonate.
Certain medications can also cause acquired renal acidosis to develop.
Diagnosis of hyperchloremic acidosis of the kidneys
Unlike patients with distal renal acidosis, those with proximal tubulopathy retain the ability to lower urine pH to below 5.5.
In order to diagnose the disease, it is necessary to show the lack of reabsorption of bicarbonate. The diagnosis is confirmed by a test to assess the level of bicarbonate.
The evaluation test shows an excessive increase in urinary bicarbonate excretion and also in urine pH as plasma bicarbonate rises above the renal threshold.
For correct diagnosis, it is also necessary to exclude other hereditary proximal tubulopathies. These include disorders such as the oculo-cerebrovascular syndrome, Dent’s disease, and glycogen storage disease due to GLUT2 deficiency.
Laboratory tests may also ask for an arterial blood gas and electrolyte analysis to confirm hyperchloraemic renal acidosis.
In addition, you can order a Basic Metabolic Panel, which consists of a group of blood tests that measure sodium and potassium levels, kidney function, and other chemicals . As part of the diagnosis, urine pH, blood and urine ketone levels, and lactic acid levels are also assessed.
This suite of tests can also help determine if the acidosis is due to a respiratory problem or a metabolic problem.
Kidney acidosis – what it is treated like
Treatment of hyperchloraemic renal acidosis depends on the cause of the disease. Hereditary proximal renal acidosis requires lifelong bicarbonate replacement therapy.
To apply this treatment method, a large amount of bicarbonate is needed to be able to normalize the serum bicarbonate level.
In some cases, diuretics are used, i.e. diuretics from the thiazide family in doses of 25-50 mg per day. For example, hydrochlorothiazide. This is done in order to improve the reabsorption of bicarbonate and thus reduce the level of the necessary amount of bicarbonate supplied from the outside.
It is also necessary to monitor the level of potassium in the plasma, so in some cases it is necessary to administer a mixture of sodium bicarbonate and potassium salts.
Generally, drug-induced hyperchloraemic proximal renal acidosis is reversible upon discontinuation of the drug. The prognosis for this disorder is generally good with proper treatment.